Ozempic (semaglutide) is a prescription medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as GLP-1 receptor agonists. It is primarily used to manage blood sugar levels in adults with type 2 diabetes, but it has also gained popularity for its effectiveness in promoting weight loss. This article delves into the mechanisms by which Ozempic works, its impact on various organs, its effectiveness in weight management, and other pertinent questions related to its use.
What is Ozempic and How Does it Work?
Ozempic (semaglutide) is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists. GLP-1 is a hormone naturally produced in the intestine that plays a critical role in regulating blood sugar levels. When you eat, GLP-1 is released and has several actions: it stimulates insulin secretion, inhibits glucagon release, slows gastric emptying, and reduces appetite. Ozempic mimics the action of GLP-1, thereby enhancing the body’s natural ability to regulate blood sugar.
Mechanism of Action
Stimulation of Insulin Secretion:
Insulin Secretion Enhancement: Ozempic enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. This means that when blood glucose levels are high, Ozempic stimulates the pancreas to release more insulin, which helps lower blood sugar levels. This mechanism is glucose-dependent, meaning it primarily works when blood glucose is elevated, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
Inhibition of Glucagon Release:
Glucagon Reduction: Glucagon is a hormone that raises blood sugar levels by stimulating the liver to release stored glucose. Ozempic reduces glucagon secretion from the alpha cells of the pancreas. By inhibiting glucagon, Ozempic decreases the amount of glucose released into the bloodstream, contributing to lower blood sugar levels, particularly after meals.
Slowing Gastric Emptying:
Delayed Gastric Emptying: Ozempic delays the emptying of stomach contents into the small intestine. This slowed gastric emptying rate means that glucose is absorbed more gradually into the bloodstream, leading to a reduction in postprandial (after-meal) blood sugar spikes. This helps in maintaining more stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Appetite Suppression:
Central Appetite Regulation: Ozempic acts on GLP-1 receptors in the brain, particularly in the hypothalamus, a region that regulates appetite and food intake. By activating these receptors, Ozempic reduces hunger and increases feelings of fullness (satiety). This leads to a decrease in overall caloric intake, which can contribute to weight loss.
Ozempic is a GLP-1 receptor agonist that effectively mimics the action of the natural hormone GLP-1. Its multifaceted mechanism of action includes enhancing insulin secretion, inhibiting glucagon release, slowing gastric emptying, and suppressing appetite.
These combined effects make Ozempic a powerful tool in managing blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes and promoting weight loss. By addressing both glucose regulation and appetite control, Ozempic helps individuals achieve better metabolic health and maintain a healthier weight.
How Does Ozempic Work to Lose Weight?

Ozempic has been found to be effective in promoting weight loss, even in individuals without diabetes. The primary mechanisms by which Ozempic aids in weight loss are:
- Appetite Suppression: Ozempic acts on the hypothalamus, the brain region that regulates appetite. It increases the feeling of fullness and reduces hunger, leading to decreased caloric intake.
- Slowed Gastric Emptying: By slowing the rate at which food leaves the stomach, Ozempic prolongs the feeling of fullness after meals, reducing overall food intake.
- Reduced Food Cravings: Users of Ozempic often report a reduction in food cravings, particularly for high-fat and high-sugar foods.
How Much Weight Can You Lose in a Month on Ozempic?
The amount of weight loss can vary significantly among individuals. Clinical studies have shown that patients using Ozempic can lose an average of 5-10% of their body weight over a period of 6 months to a year. In the first month, weight loss can range from a few pounds to more substantial amounts, depending on factors such as diet, exercise, and individual metabolic response.
What Does Ozempic Do to Your Organs?
Ozempic exerts its effects on various organs in the body:
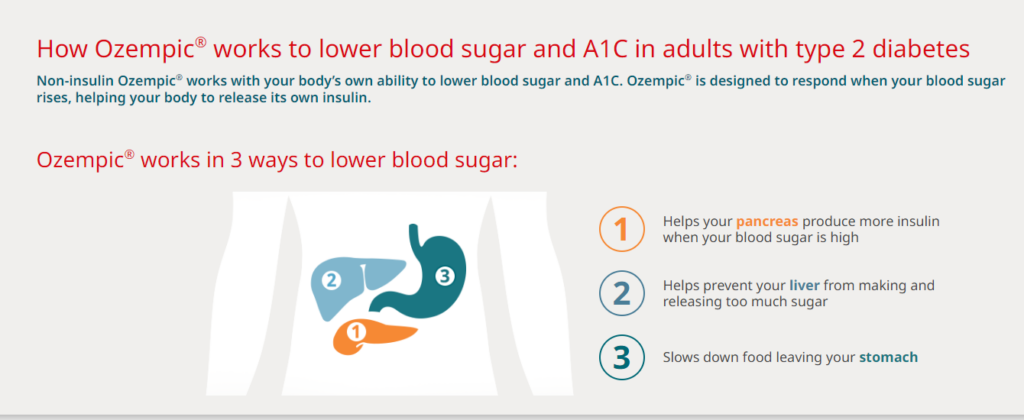
- Pancreas: Stimulates insulin release and reduces glucagon production, improving blood sugar control.
- Liver: Decreases glucose production by lowering glucagon levels.
- Stomach: Slows gastric emptying, helping to control blood sugar spikes and promote satiety.
- Brain: Acts on appetite-regulating centers to reduce hunger and food intake.
What is the Downside to Ozempic?
While Ozempic is effective in managing blood sugar and promoting weight loss, it is not without potential downsides:
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation.
- Risk of Hypoglycemia: Although rare, especially when not combined with other diabetes medications, there is a risk of low blood sugar.
- Pancreatitis: There have been reports of pancreatitis in patients using GLP-1 receptor agonists, including Ozempic.
- Gallbladder Issues: Some users may experience gallbladder-related problems such as gallstones.
How Does Ozempic Work for PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is often associated with insulin resistance and obesity. Ozempic can help manage PCOS by:
- Improving Insulin Sensitivity: By lowering blood sugar and improving insulin sensitivity, Ozempic helps manage the metabolic aspects of PCOS.
- Weight Loss: The appetite-suppressing and weight loss effects of Ozempic can help reduce the severity of PCOS symptoms.
How Quickly Does Ozempic Work?
The onset of action for Ozempic varies, but many users begin to see improvements in blood sugar levels within the first week of starting the medication. Significant weight loss effects may become noticeable within a few weeks to a few months of consistent use.
How Does Ozempic Work for Type 1 Diabetes?
Ozempic is not typically used for type 1 diabetes, as it requires functioning beta cells to stimulate insulin production. Type 1 diabetes involves the destruction of these cells, making GLP-1 receptor agonists less effective. However, some research suggests potential benefits in certain off-label cases.
How Long Does Ozempic Work?
Ozempic (semaglutide) has a long half-life of approximately one week, allowing for convenient once-weekly dosing. This extended half-life means that its effects on blood sugar levels and appetite suppression are sustained throughout the week.
After an injection, Ozempic begins to work by enhancing insulin secretion in response to meals and reducing glucagon release, which helps in managing blood sugar levels consistently.
Additionally, Ozempic slows gastric emptying and suppresses appetite, contributing to prolonged satiety and reduced caloric intake. These effects combine to provide consistent and effective management of both blood sugar levels and weight with fewer injections, making it a convenient option for long-term use.
Ozempic Side Effects
Common side effects of Ozempic include:
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation are common, especially when first starting the medication.
- Hypoglycemia: Rare but possible, particularly if used with other diabetes medications.
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas has been reported.
- Gallbladder Issues: Including the development of gallstones.
6 Week Plan Ozempic Weight Loss Results
A 6-week weight loss plan using Ozempic (semaglutide) can lead to noticeable changes in weight, especially when combined with a balanced diet and regular exercise. On average, individuals might expect to lose between 5-10 pounds over this period. Here’s a detailed breakdown of what to expect:
Week 1-2: Initial Adjustments
- Medication Onset: During the first two weeks, the body adjusts to Ozempic. Some users may experience mild gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, which typically subside as the body adapts.
- Appetite Suppression: Appetite suppression begins as Ozempic activates GLP-1 receptors in the brain, reducing hunger and promoting a feeling of fullness.
- Gastric Emptying: The medication slows gastric emptying, which helps in extending the feeling of satiety after meals.
Week 3-4: Notable Changes
- Caloric Intake Reduction: By this stage, users often report a significant decrease in daily caloric intake due to reduced appetite and fewer cravings for high-calorie foods.
- Initial Weight Loss: Early weight loss is noticeable, with an average loss of 2-4 pounds. This can vary based on individual adherence to dietary recommendations and activity levels.
- Improved Energy Levels: Some users may begin to feel more energetic as their body adjusts to a healthier caloric balance.
Week 5-6: Sustained Progress
- Steady Weight Loss: Continued use of Ozempic, combined with a healthy diet and exercise, can lead to a steady weight loss, bringing the total to approximately 5-10 pounds by the end of six weeks.
- Enhanced Satiety: The prolonged feeling of fullness and satisfaction with smaller meal portions becomes more consistent, supporting ongoing weight management.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: By this point, many users have established new, healthier eating habits and incorporated regular physical activity into their routines, which enhances the weight loss effects of Ozempic.
A 6-week plan with Ozempic can result in an average weight loss of 5-10 pounds, contingent upon consistent medication use, a balanced diet, and regular physical activity. The medication’s effects on appetite suppression, reduced cravings, and slowed gastric emptying contribute to this gradual and sustainable weight loss. Regular monitoring and support from a healthcare provider can optimize outcomes and help manage any side effects.
What Hormone Does Ozempic Mimic?
Ozempic mimics the action of the hormone GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1). GLP-1 is an incretin hormone produced in the intestine in response to food intake. It plays a critical role in glucose metabolism and appetite regulation by enhancing insulin secretion from the pancreas in a glucose-dependent manner, inhibiting glucagon release, and promoting a feeling of satiety by acting on the central nervous system. This multifaceted approach helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduce caloric intake, which is crucial for both diabetes management and weight loss.
Is Ozempic Insulin?
No, Ozempic is not insulin. Ozempic is a GLP-1 receptor agonist that works by enhancing the body’s natural ability to produce insulin when blood sugar levels are high. It stimulates insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells in a glucose-dependent manner and inhibits the release of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels by promoting glucose production in the liver. By improving the efficiency of insulin production and reducing hepatic glucose output, Ozempic helps maintain better blood sugar control without directly introducing insulin into the body.
Is Ozempic Safe?
Ozempic is generally considered safe when used as prescribed. However, it is essential to be aware of potential side effects and contraindications. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation, especially when starting the medication. There are also potential risks of pancreatitis and gallbladder issues, although these are relatively rare. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is crucial to ensure the safe and effective use of Ozempic, especially for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking other medications.
How Does Ozempic Work for Insulin Resistance?
Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Ozempic helps improve insulin sensitivity by enhancing the body’s natural insulin response. It stimulates insulin secretion from the pancreas when blood glucose levels are high and inhibits glucagon release, which reduces glucose production by the liver. This dual action helps lower blood sugar levels and improves overall glucose metabolism. For individuals with insulin resistance, particularly those with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome, Ozempic can be an effective treatment to enhance insulin sensitivity and manage blood sugar levels more effectively.
How Does Ozempic Work for Non-Diabetics?
For non-diabetics, Ozempic is primarily used for weight management. It promotes weight loss by reducing appetite and increasing satiety. Ozempic acts on the GLP-1 receptors in the brain, particularly in the hypothalamus, which regulates hunger and satiety signals. By enhancing the feeling of fullness and reducing hunger, Ozempic helps decrease overall caloric intake. This can be especially beneficial for obese or overweight individuals looking to manage their weight effectively.
How Does Ozempic Work in the Brain?
Ozempic works in the brain by acting on GLP-1 receptors located in the hypothalamus, a key brain region involved in hunger and satiety regulation. When these receptors are activated, they help reduce appetite and increase feelings of fullness (satiety). This effect is achieved by modulating the neural pathways that control hunger signals, leading to a decrease in food intake and an increase in satiety. By influencing these brain mechanisms, Ozempic helps individuals feel satisfied with smaller amounts of food, supporting weight loss and better appetite control.
How Quickly Does Ozempic Work for Weight Loss?
The weight loss effects of Ozempic can often be observed within a few weeks of starting the medication. Initial weight loss is usually due to reduced appetite and caloric intake. More significant and sustained weight loss results typically become evident over several months of consistent use. Clinical studies have shown that patients can achieve substantial weight loss with continued use of Ozempic, particularly when combined with lifestyle modifications such as a healthy diet and regular exercise.
How Soon Does Ozempic Work After Injection?
The effects of Ozempic on blood sugar levels can be observed within the first week of injection. The medication’s action on GLP-1 receptors begins to enhance insulin secretion and inhibit glucagon release shortly after administration. Continuous improvements in blood sugar control and appetite regulation can be seen over time with regular weekly injections. Most patients start experiencing noticeable benefits within the first few weeks of treatment.
How Well Does Ozempic Work for Weight Loss?
Ozempic is highly effective for weight loss, especially when combined with lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet and regular exercise. Clinical trials have demonstrated significant weight loss in individuals using Ozempic compared to those using a placebo. Patients often experience an average weight loss of 5-10% of their body weight over a period of several months. The effectiveness of Ozempic for weight loss is attributed to its dual action of reducing appetite and increasing satiety, making it a valuable tool for managing obesity and overweight conditions.
Conclusion
Ozempic is a versatile medication that offers significant benefits for managing type 2 diabetes and promoting weight loss. By mimicking the action of the GLP-1 hormone, it helps regulate blood sugar levels, reduce appetite, and promote satiety. While it has some potential side effects and is not suitable for everyone, it remains a valuable tool in the treatment of metabolic disorders. For individuals considering Ozempic, consulting with a healthcare provider is essential to ensure its safety and effectiveness in their specific case.
